TBAnnotationClustering 源码浅析
在地图上展示标注点是一个比较常见的需求,展示成百上千个标注点也不奇怪。我之前公司有做一款公共出行 app,需要在地图上展示上千个公共自行车标注点(光杭州地区)。
我们用的是百度地图 SDK,添加完之后,滑动起来就非常卡顿。百度地图 SDK 显然不支持在加载这么多标注点后还能保证流畅滑动。它之后确实也有了用 quad tree 来处理标注点的接口,但我们当初用的时候还没有提供。当初在调研解决方案的时候,就看到了 TBAnnotationClustering 1 这篇文章。我在会议上也提出了这种解决方案,但当时也有其他考量没有采用,只是简单处理了添加新的标注点的时候,不移除重复区域的标注点。
看到这样精巧的数据结构设计,也很好奇是原理是什么,但是当初水平有限,没有完全看懂。不过这件事情我一直惦记着,现在三年后,终于花时间去一行一行理解代码。
下面就是我对 TBAnnotationClustering 的源码浅析,采用 Top-down 的方式看源码。
前置知识
在看源码之前,我们需要有一些前置知识。了解经纬度坐标系,MKMapRect,TBBoundingBox 之间是怎样的关系,以及如何相互转换。
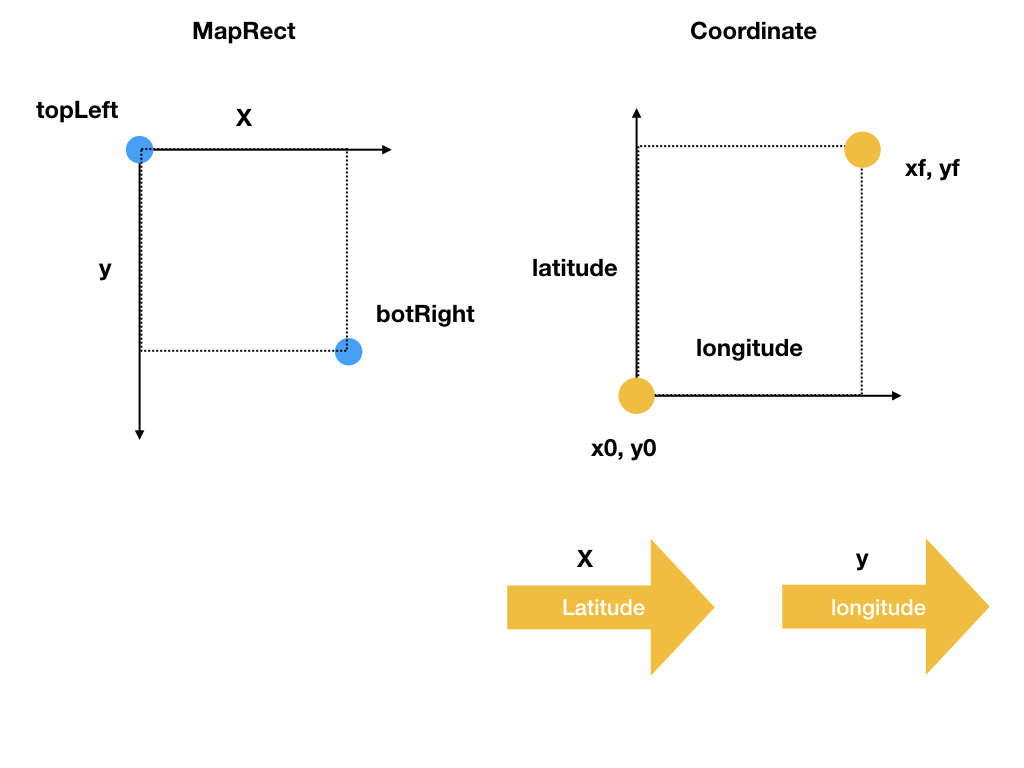
左边是 MKMapRect 的示例,右边是经纬度在平面投影的坐标系。向右 longitude 增长,向上 latitude 增长。下面详细讲解这些结构。
-
经纬度坐标就是我们熟悉的经纬度2。
-
MKMapRect是MapKit提供的结构,是在二维地图上投影的矩形,origin是左上角的坐标,size就是地图的长宽,单位都是MKMapPoint。因为地图涉及到缩放的原因,
MKMapPoint跟 screen 上的 point 并不是一一对应关系。这中间涉及到一个MKZoomScale的概念:MKZoomScale provides a conversion factor between MKMapPoints and screen points.
When MKZoomScale = 1, 1 screen point = 1 MKMapPoint. When MKZoomScale is
0.5, 1 screen point = 2 MKMapPoints.
所以,
MKMapPoint是MapKit提供的一个抽象单位,它跟 screen 上的坐标根据MKZoomScal有相应的转换关系。对地理坐标也可以根据MKCoordinateForMapPoint(),MKMapPointForCoordinate()进行相互转换。 -
typedef struct { MKMapPoint origin; MKMapSize size; } MKMapRect; -
TBBoudningBox是 TBAnnotationClustering 的一个结构,用来表示一个区域。(x0, y0),和 (xf,yf) 是组成TBBoundingBox的两个坐标点,(x0, y0) 是这个区域经纬度最小的坐标,(xf, yf) 是最大的坐标。需要注意的是,TBBoundingBox在这个坐标系中的时候, x 是在 latitude 方向上的。typedef struct TBBoundingBox { double x0; double y0; double xf; double yf; } TBBoundingBox;TBBoundingBoxForMapRect()可以把MKMapRect转换到TBBoudingBox。TBBoundingBox TBBoundingBoxForMapRect(MKMapRect mapRect) { CLLocationCoordinate2D topLeft = MKCoordinateForMapPoint(mapRect.origin); CLLocationCoordinate2D botRight = MKCoordinateForMapPoint(MKMapPointMake(MKMapRectGetMaxX(mapRect), MKMapRectGetMaxY(mapRect))); CLLocationDegrees minLat = botRight.latitude; CLLocationDegrees maxLat = topLeft.latitude; CLLocationDegrees minLon = topLeft.longitude; CLLocationDegrees maxLon = botRight.longitude; return TBBoundingBoxMake(minLat, minLon, maxLat, maxLon); }TBMapRectForBoundingBox()是把 BoundingBox 转换成 MKMapRect 的函数。先把 (x0, y0), (xf,yf) 转换成MKMapPoint,然后得到 origin(图中 topLeft 的位置) 的坐标和 width, height。MKMapRect TBMapRectForBoundingBox(TBBoundingBox boundingBox) { MKMapPoint topLeft = MKMapPointForCoordinate(CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(boundingBox.x0, boundingBox.y0)); MKMapPoint botRight = MKMapPointForCoordinate(CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(boundingBox.xf, boundingBox.yf)); return MKMapRectMake(topLeft.x, botRight.y, fabs(botRight.x - topLeft.x), fabs(botRight.y - topLeft.y)); }
总结一下,对于地图上的一个区域的表示,MKMapKit 用 MKMapRect 来表达,TBAnnotationClustering 用 TBBoudningBox 来表达。这三者之间可以相互转换。
数据处理
从 TBMapViewController.m 中 [self.coordinateQuadTree buildTree]开始。
首先从一个记录了大约 8w 多个标注点的文件中建立 TBQuadTreeNodeData 数组。这些标注点的范围可以参考下面的图片:
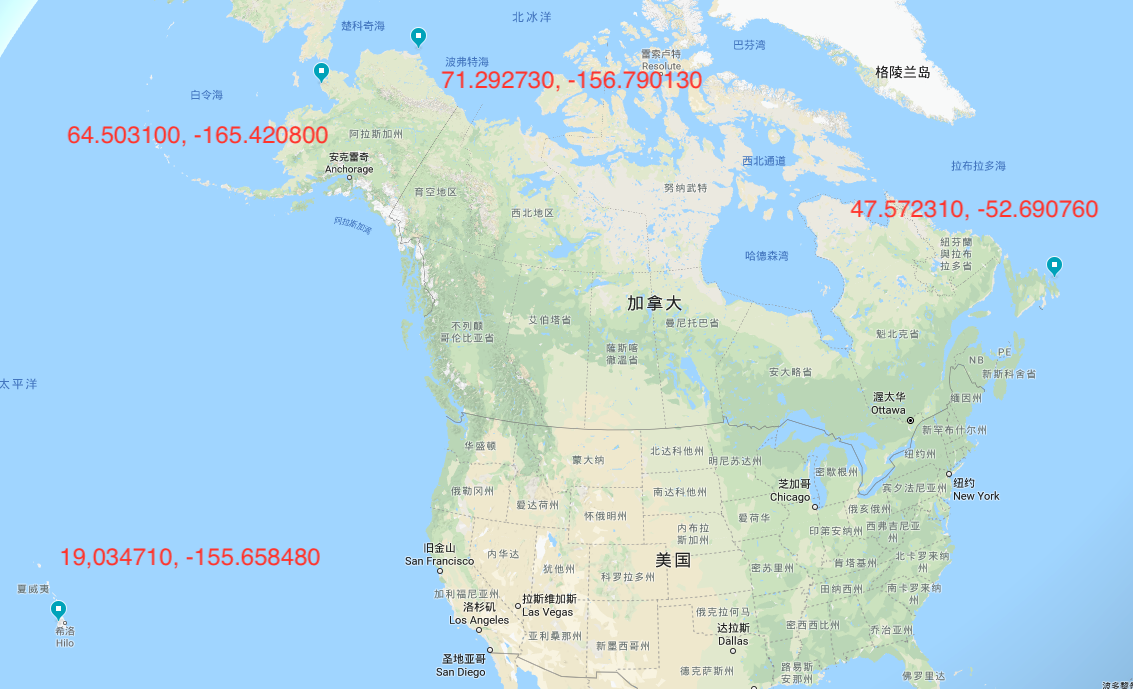
标注点四个经纬度极值坐标
-
East most (47.572310, -52.690760)
-
North most (71.292730, -156.790130)
-
South most (19,034710, -155.658480)
-
West most (64.503100, -165.420800)
(19, -166) most south-west (72, -53) most north-east
数据集坐标范围(longitude: -165.4208, -52.69076; latitude: 19.03471, 71.29273)
创建一个包含所有坐标点的区域 world。不太清楚这个 -53 经度(比 -52.69076 小 )是什么意思。
TBBoundingBox world = TBBoundingBoxMake(19, -166, 72, -53);
_root = TBQuadTreeBuildWithData(dataArray, count, world, 4);
标注点数据用下面的结构体表示:
typedef struct TBQuadTreeNodeData {
double x; // latitude
double y; // longitude
void *data;
} TBQuadTreeNodeData;
Construct Quad Tree
有了所有的标注点后,下面就是构造 QuadTree3 来存储这些数据。QuadTree 的查询复杂度可以在 O(log n) 内。
调用 TBQuadTreeBuildWithData(TBQuadTreeNodeData *data, int count, TBBoundingBox boundingBox, int capacity) 构建。
data 是标注点数组,count 是数组数量,boudingBox 就是上面描述的包含所有标注点的区域,capacity 是每一个区域的容量。
TBQuadTreeNode* TBQuadTreeBuildWithData(TBQuadTreeNodeData *data, int count, TBBoundingBox boundingBox, int capacity)
{
TBQuadTreeNode* root = TBQuadTreeNodeMake(boundingBox, capacity);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData(root, data[i]);
}
return root;
}
Insert Node
插入 data 到 node 中。
这是 node 的数据结构,有四个方向(西北,东北,西南,东南)的 child node,一个表示该 node 范围的 boundingBox,容量 bucketCapacity,当前数量 count,实际存储的数据 points。
typedef struct quadTreeNode {
struct quadTreeNode *northWest;
struct quadTreeNode *northEast;
struct quadTreeNode *southWest;
struct quadTreeNode *southEast;
TBBoundingBox boundingBox;
int bucketCapacity;
TBQuadTreeNodeData *points;
int count;
} TBQuadTreeNode;
通过 dfs 的形式遍历 quad tree,先用TBBoundingBoxContainsData() 判断 data 坐标是否在 node 的 boundingbox 范围内,如果未超出容量 capacity,则插入 data,否则对四个方向的节点递归调用 TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData。在递归调用前,如果 node 还未被拆分,则调用 TBQuadTreeNodeSubdivide() 函数拆分这个 node,拆分就是把 boundingBox 拆成四等份,赋给相应的四个方向的 child node。这样执行完,就把所有的数据插入到了构造的 quad tree 中了。
bool TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData(TBQuadTreeNode* node, TBQuadTreeNodeData data)
{
if (!TBBoundingBoxContainsData(node->boundingBox, data)) {
return false;
}
if (node->count < node->bucketCapacity) {
node->points[node->count++] = data;
return true;
}
// Check to see if the current node is a leaf, if it is, split
if (node->northWest == NULL) {
TBQuadTreeNodeSubdivide(node);
}
// Traverse the tree
if (TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData(node->northWest, data)) return true;
if (TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData(node->northEast, data)) return true;
if (TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData(node->southWest, data)) return true;
if (TBQuadTreeNodeInsertData(node->southEast, data)) return true;
return false;
}
拆分
void TBQuadTreeNodeSubdivide(TBQuadTreeNode* node)
{
TBBoundingBox box = node->boundingBox;
double xMid = (box.xf + box.x0) / 2.0;
double yMid = (box.yf + box.y0) / 2.0;
TBBoundingBox northWest = TBBoundingBoxMake(box.x0, box.y0, xMid, yMid);
node->northWest = TBQuadTreeNodeMake(northWest, node->bucketCapacity);
TBBoundingBox northEast = TBBoundingBoxMake(xMid, box.y0, box.xf, yMid);
node->northEast = TBQuadTreeNodeMake(northEast, node->bucketCapacity);
TBBoundingBox southWest = TBBoundingBoxMake(box.x0, yMid, xMid, box.yf);
node->southWest = TBQuadTreeNodeMake(southWest, node->bucketCapacity);
TBBoundingBox southEast = TBBoundingBoxMake(xMid, yMid, box.xf, box.yf);
node->southEast = TBQuadTreeNodeMake(southEast, node->bucketCapacity);
}
Clustering
整体思路是把 mapRect 按 cellSize 来划分,遍历 mapRect 下的所有 cell,每个 cell 对应一个 MKMapRect 矩形,转换成 boundingBox,统计该 boundingBox 下的所有标注点,如果大于一个,取平均坐标并添加一个标注点,否则添加该标注点,保证一个 cell 只有一个标注点。
clutering 的代码精简后:
- (NSArray *)clusteredAnnotationsWithinMapRect:(MKMapRect)rect withZoomScale:(double)zoomScale
{
double TBCellSize = TBCellSizeForZoomScale(zoomScale);
double scaleFactor = zoomScale / TBCellSize;
// map points 转换到 screen points,单位坐标跨度为 TBCellSize
NSInteger minX = floor(MKMapRectGetMinX(rect) * scaleFactor);
NSInteger maxX = floor(MKMapRectGetMaxX(rect) * scaleFactor);
NSInteger minY = floor(MKMapRectGetMinY(rect) * scaleFactor);
NSInteger maxY = floor(MKMapRectGetMaxY(rect) * scaleFactor);
NSMutableArray *clusteredAnnotations = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
// 遍历 rect 范围内的所有 cell
for (NSInteger x = minX; x <= maxX; x++) {
for (NSInteger y = minY; y <= maxY; y++) {
// screen points 转换成 map points,恢复单位坐标跨度为 1
MKMapRect mapRect = MKMapRectMake(x / scaleFactor, y / scaleFactor, 1.0 / scaleFactor, 1.0 / scaleFactor);
__block double totalX = 0;
__block double totalY = 0;
__block int count = 0;
TBQuadTreeGatherDataInRange(self.root, TBBoundingBoxForMapRect(mapRect), ^(TBQuadTreeNodeData data) {
totalX += data.x;
totalY += data.y;
count++;
});
if (count == 1) {
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(totalX, totalY);
TBClusterAnnotation *annotation = [[TBClusterAnnotation alloc] initWithCoordinate:coordinate count:count];
[clusteredAnnotations addObject:annotation];
}
if (count > 1) {
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(totalX / count, totalY / count);
TBClusterAnnotation *annotation = [[TBClusterAnnotation alloc] initWithCoordinate:coordinate count:count];
[clusteredAnnotations addObject:annotation];
}
}
}
return [NSArray arrayWithArray:clusteredAnnotations];
}
下面详细讲解
zoomScale
zoomScale 的定义如下:
double scale = mapView.bounds.size.width / mapView.visibleMapRect.size.width;
所以 MapPoint length = ScreenPoint length / Scale
实测 zoomScale(0, 大概1.4),所以 zoomScale 越大,地图可视区域范围越小。
ZoomLevel
这里把 MKMapSizeWorld.width 按照 256 的大小计算出数量,然后用调用 log2 来设置一个最大的缩放级别(zoomLevelAtMaxZoom)。
根据 ` NSInteger zoomLevel = MAX(0, zoomLevelAtMaxZoom + floor(log2f(scale) + 0.5));`
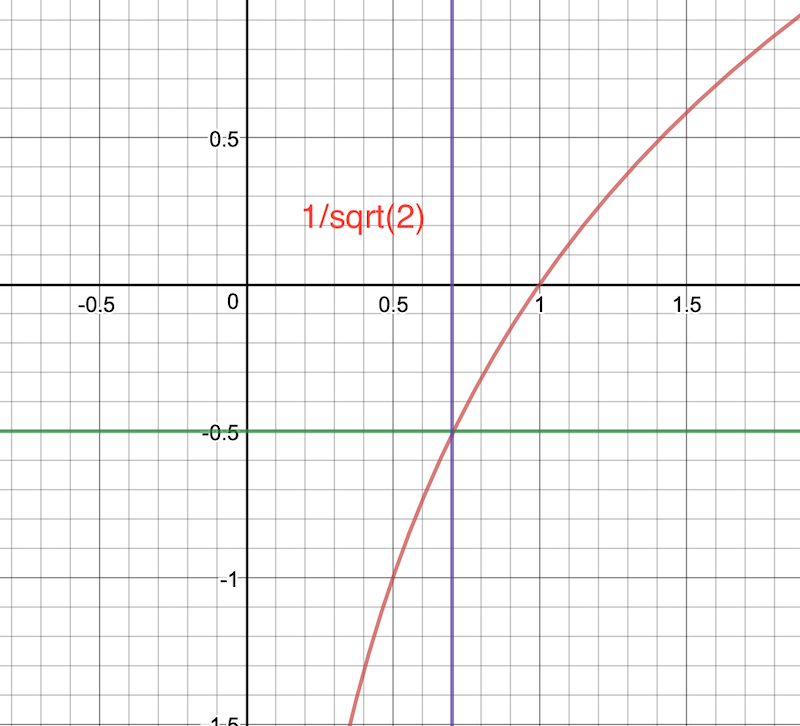
log2f 函数
scale 的范围分这两种情况:
- (0, 1/sqrt(2))
0 <= zoomLevel < zoomLevelAtMaxZoom
- [1/sqrt(2), sqrt(2))
zoomLevel = zoomLevelAtMaxZoom
1/sqrt(2) 是 log2f(scale) = -0.5 的情况,此时的缩放级别刚好是最大缩放级别(zoomLevelAtMaxZoom)。因为 scale 会小于 sqrt(2)(根据测试),所以最大的缩放级别也不会超过 zoomLevelAtMaxZoom。因为实际初始的的 scale 为 0.000015,所以实际的 zoomLevel 范围为 [4-20]。
NSInteger TBZoomScaleToZoomLevel(MKZoomScale scale)
{
double totalTilesAtMaxZoom = MKMapSizeWorld.width / 256.0;
NSInteger zoomLevelAtMaxZoom = log2(totalTilesAtMaxZoom);
NSInteger zoomLevel = MAX(0, zoomLevelAtMaxZoom + floor(log2f(scale) + 0.5));
return zoomLevel;
}
CellSize
地图在缩放的时候,会根据缩放级别划分不同大小的区域 cellSize。
float TBCellSizeForZoomScale(MKZoomScale zoomScale)
{
NSInteger zoomLevel = TBZoomScaleToZoomLevel(zoomScale);
switch (zoomLevel) {
case 13:
case 14:
case 15:
return 64;
case 16:
case 17:
case 18:
return 32;
case 19:
return 16;
default:
return 88;
}
}
cellSize 是正方形,是以 screen points 来计量的,表示的是 clustering 的一个区域,该区域内所有的标注点都聚集成一个标注点。cellSize 越小,地图划分的越精细。可以看到,从 13-19 的时候,cellSize 逐渐变小,意味着需要减小 clustering 区域的大小,来显示更多的点。
缩放级别在 4-12 的时候,此时缩放级别较小,不需要显示太多的标注点,所以用最大的 cellSize。
在缩放级别为 20 的时候,此时每个点都需要显示出来,此时的 scale 为 0.804436 左右,88/scale = 109 map points。通过 MKMetersBetweenMapPoints() 可以得到两个 mapPoint 的距离大概在 0.012837 m。所以 88 的 cellzie 在 20 zoomLevel 下大概是 1.5m。
这是 scale 对应 cellSize 关系
| scale | cellSize | cellSizeInMeters |
|---|---|---|
| 0.804436 | 88 | 1.5 |
| 0.500000 | 16 | 0.41 |
| 0.250000 | 32 | 1.64 |
| 0.028035 | 64 | 29.3 |
| 0.000015 | 88 | 75,310 |
值得注意的是,zoomLevel 为 19,也就是 cellSize 为 16 的时候,反而 cellSize 实际的范围是最小的,而不是 zoomLevel 是 20 的时候,不知道作者这里的考量是什么,我觉得最大的 zoomLevel 应该是最小的 cellSize。
diff 更新
- (void)updateMapViewAnnotationsWithAnnotations:(NSArray *)annotations
{
NSMutableSet *before = [NSMutableSet setWithArray:self.mapView.annotations];
[before removeObject:[self.mapView userLocation]];
NSSet *after = [NSSet setWithArray:annotations];
NSMutableSet *toKeep = [NSMutableSet setWithSet:before];
[toKeep intersectSet:after];
NSMutableSet *toAdd = [NSMutableSet setWithSet:after];
[toAdd minusSet:toKeep];
NSMutableSet *toRemove = [NSMutableSet setWithSet:before];
[toRemove minusSet:after];
[[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] addOperationWithBlock:^{
[self.mapView addAnnotations:[toAdd allObjects]];
[self.mapView removeAnnotations:[toRemove allObjects]];
}];
}
在移动地图的时候,目标区域很大概率会与当前区域重合。我们这时候可以只添加新增的标注点,保留共同的标注点,只移除屏幕外的标注点。
缺点
我实际在测试的时候,发现当出现坐标重复的时候,比如下面两个标注点,Quality Inn By Choice Hotels(33.116990000000001, -96.098560000000006),Ramada Inn(33.116990000000001, -96.098560000000006),会重叠在一起。
总结
用 QuadTree 可以把查询复杂度限制在 O(log n) 内,极大了降低了单点查询和按区域查询的时间。这种按区域划分的方法,可以方便的加入 Clustering(聚集) 功能,从添加几千个到十几个(在较小的缩放级别下),非常显著地减少了地图渲染标注点的压力。
不过重叠问题需要单独处理,比如我们可以在最大的缩放级别下,强制不 Clustering。